-By Thupten Kelsang for Museum of Modern Art, 16 July 2025
Debates around the ownership of cultural heritage and decolonizing museums have become increasingly visible and polarizing in the public domain, leading to attempts to redefine the term “museum” itself.1 It is evident that large-scale Imperial looting campaigns such as the “Sack of Benin” (1897), the “Looting of the Summer Palace” (1860), and the “Pillage of Sri Rangapattana” (1799) have received sustained scholarly attention.2 These seminal events of British looting have been extensively researched, remain under public scrutiny, and are firmly lodged in museum agendas. However, relatively little attention has been paid (either in the public domain or museums) to the invasion of Tibet in 1903–4 by Colonel Francis Younghusband (1863–1942), even though, when compared with Benin, “more troops were involved in his mission, a larger number of buildings were raided, and greater quantities of material were removed.”3 This extreme case of British looting has received comparatively limited academic attention compared to other contexts.4
While Tibet has ceased to exist as an independent nation, Tibetan material heritage continues to be extensively circulated, collected, displayed, and interpreted in museums, the art market, and academia (fig. 1). Exhibitions of “Tibetan art” remain a regular occurrence in the exhibition circuit. Moreover, Tibetan objects are omnipresent in auctions of Asian art every season at all the major international auction houses and continue to fetch record prices in the global art market. This hypervisibility of Tibetan objects in museums and the market raises a fundamental question: Why is so much of Tibet’s material heritage circulating outside Tibet, displaced from its original place of worship and practice, and so far removed from Tibetans? This phenomenon is succinctly captured by Clare Harris, who notes, “The bulk of Tibet’s portable cultural heritage has been retained everywhere other than Tibet, and is now most readily at the disposal of everyone other than Tibetans.”5 Hence, further attention to the provenance of Tibetan collections dispersed across the world in public and private collections is warranted, particularly to assess the colonial entanglement of sacred Tibetan objects.

The complex colonial entanglement of museum collections in the Global North has led to a growing body of scholarship suggesting that museums must engage with the communities to which these objects originally belonged as a form of symbolic reparation and restorative justice.6 This practice has been gaining recognition and momentum, with various attempts to “transform” the museum or, at the very least, alter the relationship between the museum and “communities of origin,” a move that has been deemed “one of the most important developments in the history of museums.”7 However, to this day, there is an acute absence of Tibetans in museums, whether as curators, interpreters, collaborators, or other agents in the construction of knowledge and representation or as members of the audience for museum displays.
“Doubly colonial” Tibet: An Inheritance of Loss
In her seminal text The Museum on the Roof of the World: Art, Politics, and the Representation of Tibet (2012), Harris highlights that the hypervisibility of Tibetan objects is due to the extensive scale of displacement of Tibetan heritage from the Tibetan landscape and people through repeated waves of extraction of objects in a “doubly colonial” context, that of both British and Chinese looting in the twentieth century.8 She articulates that Tibet is a possibly unique example of being “doubly colonial” as before the People’s Republic of China assimilated Tibet, it witnessed a British colonialist intervention in the form of the Younghusband “Expedition” of 1903–4. These repeated waves of pillaging have physically deprived Tibet of significant quantities of its material heritage, which is now found primarily in Western or Chinese museums and private collections worldwide, not in Tibet itself.
The Younghusband Mission was a British military campaign sanctioned by Lord Curzon (1859–1952), who served as viceroy of India (1898–1905), due to rising anxieties over perceived Russian influence in Tibet. There was no intention to annex Tibet into the British Empire, but the aim was to force the Tibetans to end their suspected dealings with Russia and to establish a dominant British influence in Tibet, an agenda some have deemed “almost entirely bogus.”9 Strikingly, the Younghusband Mission was primarily a military campaign, deploying the latest technology available to the British at the time: four field guns firing shrapnel shells and two Maxim machine guns capable of firing 760 rounds per minute. To illustrate the scale of senseless violence and plunder that took place during this invasion, let’s revisit the infamous “Battle of Guru,” known among Tibetans as the “Massacre of Chumik Shenko” (fig. 2).
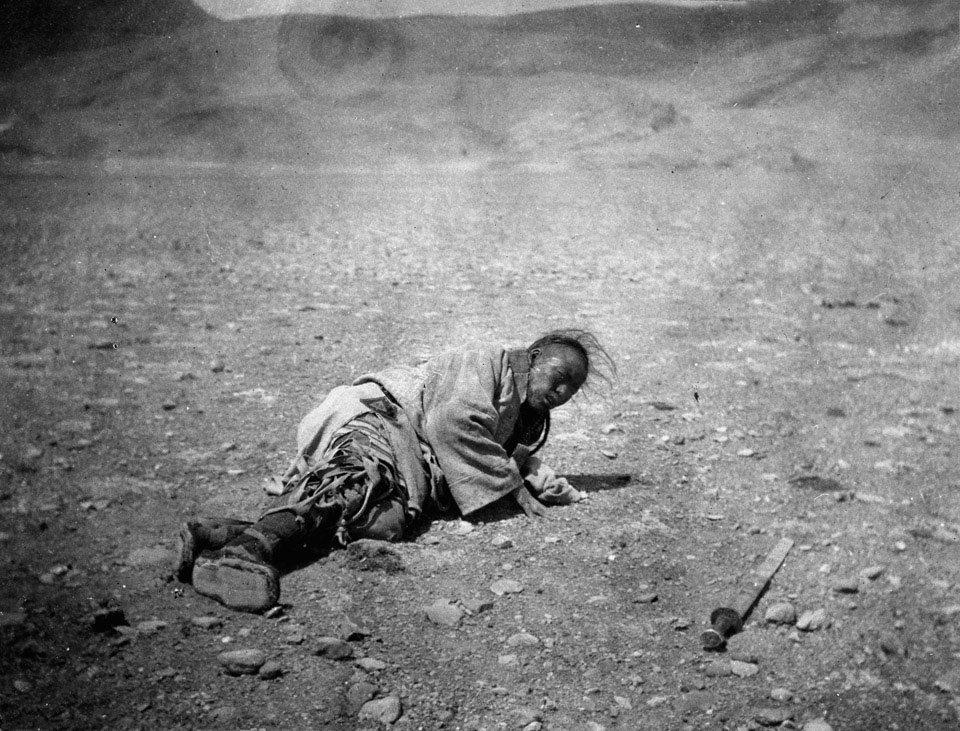

On March 31, 1904, the incursion of British forces was halted by Tibetan forces in the valley of Guru in southern Tibet. According to Tibetan sources, the British proposed that as a precondition for negotiations, all Tibetan soldiers must unload their weapons and extinguish the fuses of their muskets.10 While preparations for negotiations were taking place, British forces strategically positioned their machine guns on nearby hills and surrounded the Tibetan army from three directions. According to Tibetan government records, when the British opened fire, 523 Tibetans were killed and 300 more were wounded.11 While there is debate about what started the skirmish, it is apparent that the British army used a strategic maneuver to outflank and “box in” the Tibetan army, attacking them from three sides and firing over 15,000 rounds of ammunition on retreating Tibetans.12 British forces pursued Tibetans for 12 miles and continued to kill and maim them.13 After this massacre, many battle trophies were collected from the bodies of the dead or from surrendered Tibetan soldiers, including earrings, gau (box amulets), bandolier belts, weapons, and clothing.
After seizing key strategic positions in Tibet, such as the monastery-city of Gyantse, British officers committed what Patrick French has termed “casual robbery” in deserted monasteries or houses.14 What began as collecting battle trophies at Guru became frenzied looting among the ranks at every available opportunity, but the expedition later followed a formalized protocol to sift through the material, which would, in appearance, be “a more reputable form of collecting for intellectual pursuits.”15 According to Harris, the Younghusband Mission is significant because it created a desire and appetite for Tibetan objects in the market.16 Even before Younghusband’s military campaign reached its conclusion in Lhasa, a steady stream of looted Tibetan objects had been trickling into Great Britain, some of which fetched high prices at Christie’s auction house in London.17
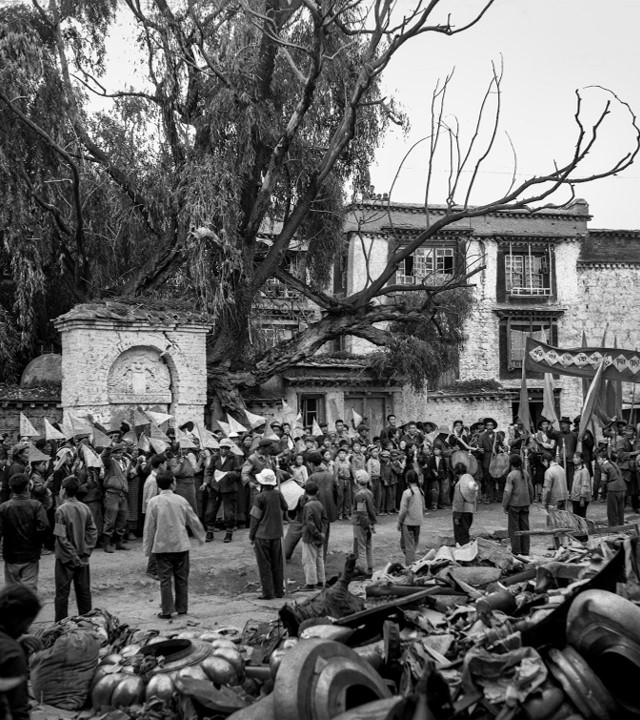

The state-led destruction of Tibetan cultural heritage peaked later, during the Cultural Revolution (1967–77), when according to Tibetan sources, more than 6,000 Tibetan temples and monasteries were ransacked and partially or fully destroyed mainly by the People’s Liberation Army (PLA) and agents of the Chinese Communist Party (CCP).18 During this purge of Tibetan culture, sacred Buddhist sites such as the Jokhang temple in Lhasa were desecrated (fig. 3). This systematic desecration was through the destruction of venerated sacred images of Buddha, Bodhisattvas and protective spirits; the burning of precious manuscripts, manuscript printing blocks and thangka paintings as cooking fuel; and the turning of the area into a pig slaughterhouse and toilet by the PLA Garrison Command.19 Sam van Schaik notes this destruction was a “carefully planned operation” as each site was first inventoried, with “all precious stones and metal objects carefully labelled and prepared for transportation to Beijing.”20 The desecration and destruction of the Jokhang temple are illustrative of what happened to many sacred temples and monasteries all over Tibet.
In an overview of different case studies on plundered cultural properties for the International Committee of Museums (ICOM) publication Countering Illicit Traffic in Cultural Goods: The Global Challenge of Protecting the World’s Heritage (2015), Sam Hardy argues that the loss and destruction of Tibetan heritage under the Chinese state was “incalculable both in terms of culture and in terms of sheer quantity.”21 For instance, in the 1990s, monasteries in Tibet were targeted by Chinese gangs who “killed monks in their violent attempts to remove statues from monasteries” so that they could profit from the appetite for Tibetan material heritage in the global art market.22 In 2008, the Chinese police confiscated cultural assets from Tibetan communities as a punishment for the Tibetan uprising, and this was evidenced by a marked flow of Tibetan cultural material onto the antiquities market.23
The destruction and dispossession of Tibetan material heritage has been acutely experienced by Tibetan refugees, who were forced to sell their material heirlooms to survive and sustain themselves. The exodus of refugees from Tibet in 1959 has only added further symbolic capital to Tibetan material culture.24 Despite the mainstreaming of debates around decolonizing museums and restitution of looted heritage, the case of Tibet in museums has remained conspicuously absent from both postcolonial and decolonial discourse.25 Tibetans remain completely marginalized within such museum agendas and discussions, giving rise to a paradox that while objects from Tibet are much desired and welcomed in museums, Tibetan people are not.26 Thus, the fractures in the geopolitical and cultural identity of the Tibetan people are further amplified as they endure the loss not only of their land but also of their material heritage.
Uncovering the “Debt of Truth” in Tibetan Collections
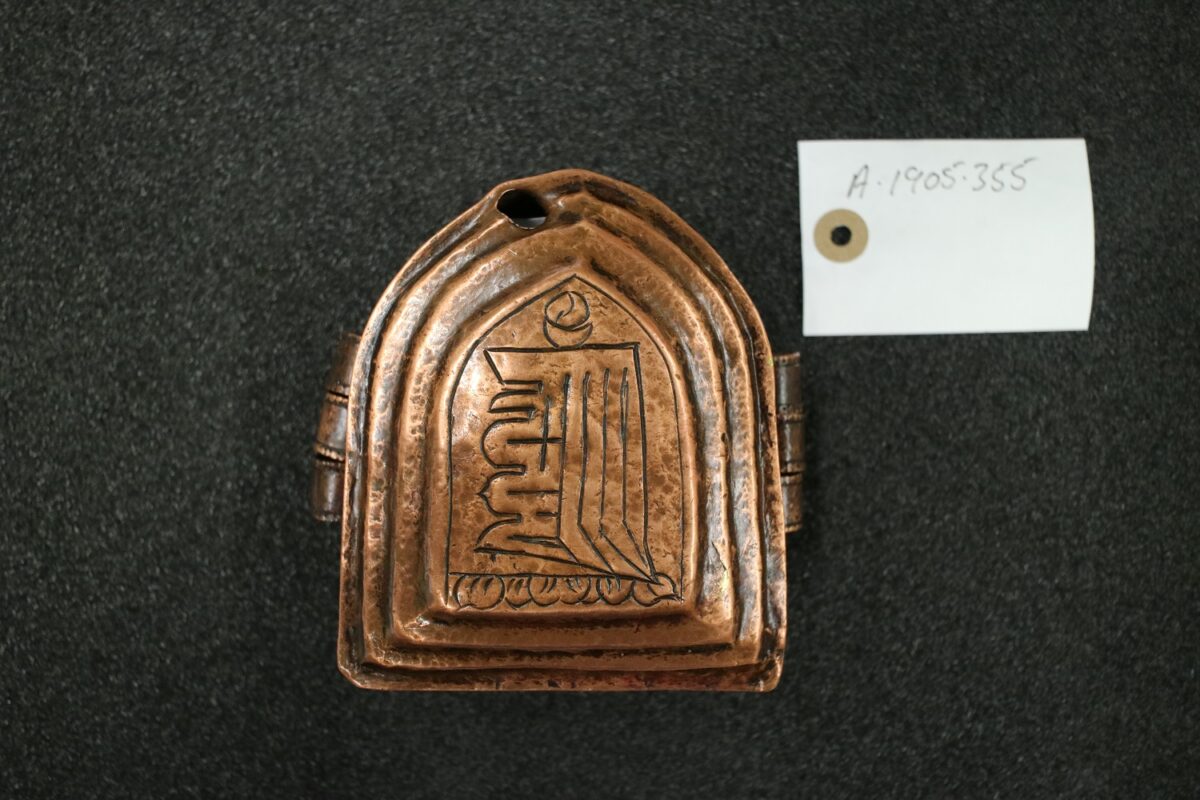
Among the vast Tibetan collections dispersed across museums and private collections in the United Kingdom lie the muted and suppressed histories of violence and plunder that took place during the Younghusband invasion of Tibet, often embedded in the object’s very materiality. This was particularly evidenced by a gau pierced by a bullet and now held in the Cheltenham Museum and Art Gallery in Gloucestershire, which Harris argues was collected as a battle trophy by the British army.27 Another gau riddled with a bullet hole (fig. 4) was discovered in the collection of the National Museums Scotland.28 The late historian of Tibetan art John Clarke highlights that for a gau to be effective, it must be in contact with the body.29 For this reason, although we do not have Tibetan bodies to examine to uncover the violence that took place during Younghusband’s military campaign in Tibet, the gau becomes a proxy for Tibetan bodies and lives in material form. During my collections research at various museums in the United Kingdom, I have encountered a vast number of gau and even if only a minority of them were removed from the bodies of dead Tibetans, this still potentially represents hundreds of lost Tibetan lives (fig. 5).
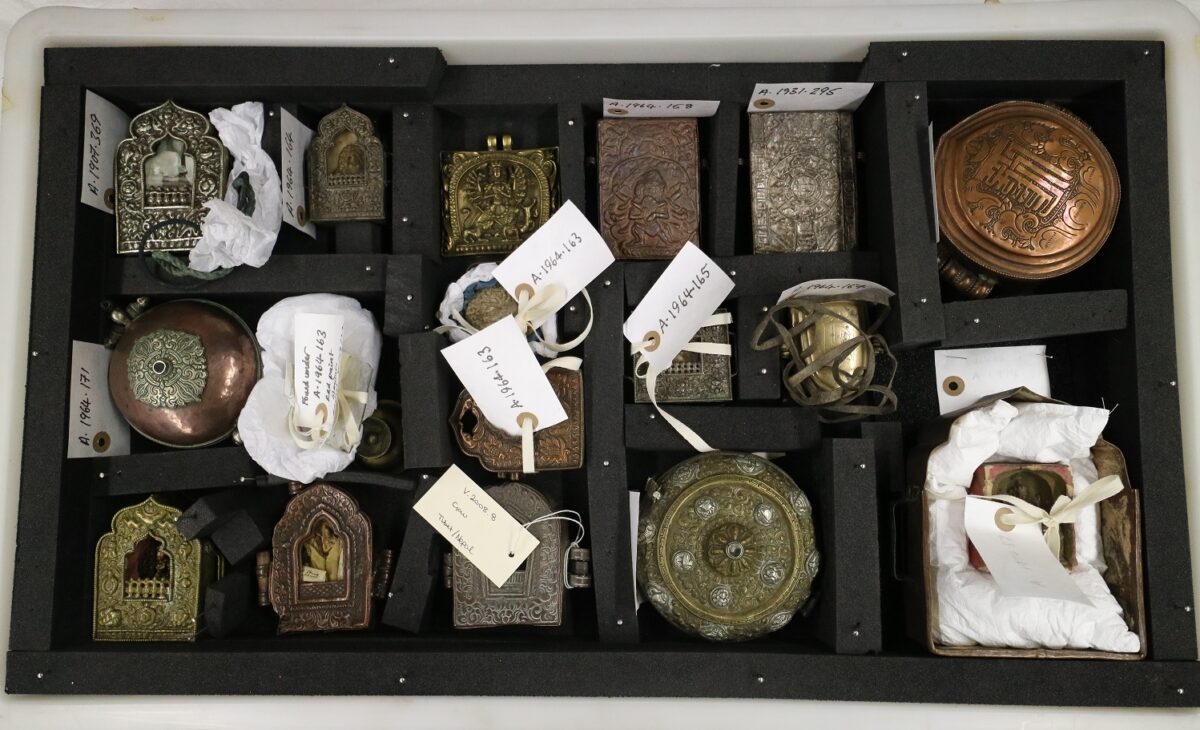


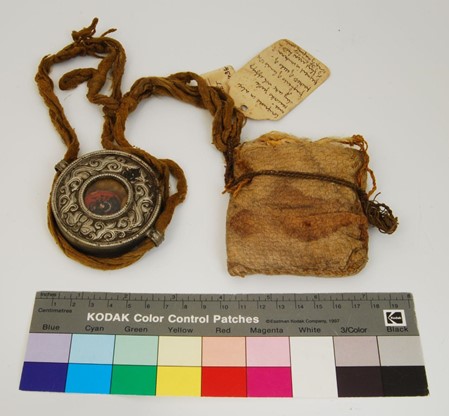
This loss of life can be even more “explicitly” evidenced through Tibetan objects I encountered during my doctoral fieldwork that have spots of what could be blood. I observed such spots on two objects, both with a direct Younghusband provenance—a gau in the World Cultures collection of the National Museums Liverpool and a wicker shield from the British Museum.30 The gau (fig. 6) houses a tsa-tsa (clay tablet) of Mahakala and a folded kha-btags (white silk scarf). The handwritten label reads, “Charm against bullet—taken from the body of a dead Tibetan at Dongste monastery by Major.”31 The label refers to a Geluk monastery at Drongtse (‘brong-rtse), near Gyantse, that was founded in 1442. On examining this gau, I observed a sizeable, red spot on the object’s textile amulet (srung-nga) component. I thought this stain was possibly blood due to the acquisition circumstances (it was taken from a dead Tibetan’s body) and the knowledge of how the amulet is traditionally worn across the body. I immediately requested testing, and the in-house investigation was conducted by senior organics conservator Tracey Seddon. Due to the museum’s hesitance to authorize destructive sampling, we discussed and explored alternative, nondestructive analytical procedures. However, such methods were inconclusive.32 Joanne Dyer and Diego Tamburini from the Department of Scientific Research at the British Museum also conducted noninvasive testing on the shield, with FORS (Fiber Optic Reflectance spectroscopy) as the only available in-house option (fig. 7). Preliminary tests on both objects were unable to conclusively scientifically verify the presence of blood, and multiple experts, including the team at the British Museum, concluded that the only viable route would be to conduct proteomics analysis (a cellular examination of proteins), which would require destructive sampling.33


Even with the small sample size of the collections review during my doctoral research, I uncovered two objects of potential significance at the British Museum whose origins were inscribed on them—a kapala (fig. 8) and a helmet (fig. 9).34 Both had been “collected” by Major H. A. Iggulden, a member of the Younghusband Mission. Upon examination, I observed that “Palkhor Chode” had been inscribed on the base of the kapala. This refers to Pelkhor Chode, an important monastic complex in Gyantse (located in the historical Tsang province of Tibet), which was attacked and occupied by the British in 1904.35 I argue that this kapala was inscribed by the field “collector” to mark the origins of this battle trophy collected from Gyantse. The helmet revealed a Tibetan inscription rgyal-tse (Gyantse), which is accompanied by what appears to be the Tibetan numeral seven (༧). I believe that these objects were removed and taken from the Pelkhor Chode monastery (or Gyantse dzong) by Major Iggulden, but were transcribed by two different types of agents: Indigenous (Tibetan) and colonial (British). However, it is noteworthy that the museum recorded neither of these easily legible inscriptions, particularly considering they reveal direct provenance. These gaps in the museum database are not highlighted to criticize the specific institutions, as this is symptomatic of the broader sector, but rather to show how such gaps could become focal points for museums to coproduce knowledge with living members of the Tibetan community, rather than re-amplifying what was said or done by British officers.


Considering the limitations in archival information (notably on early Tibetan collections), and more importantly, due to suppressed and silenced histories in the colonial archive, new modes of scientific inquiry on Tibetan objects could be deployed to uncover “truths” in the collection. Such inquiries can make the hidden violence of Tibetan objects explicit, which historian Achille Mbembe calls a “debt of truth” that museums should address.36 This case study also highlights the inherent conflict between institutional guidelines that seek to preserve the physical integrity of objects and the necessity of conducting tests that generally require destructive sampling.37 Reflecting on the histories of the museumification of Tibet’s material heritage, venerated Tibetan sacred images and objects (such as gau) have been emptied of their sacral contents (gzungs-gzhug) in the name of scientific inquiry and thangka paintings have been radically altered with their textile borders (gong-gsham) removed to elevate them as “fine art.”38 Considering sacred Tibetan objects have been subjected to such forms of museal violence across different institutions, museums must reconsider and prioritize such modes of inquiry that would uncover the colonial violence that caused the object to be in the museum’s collection in the first place.
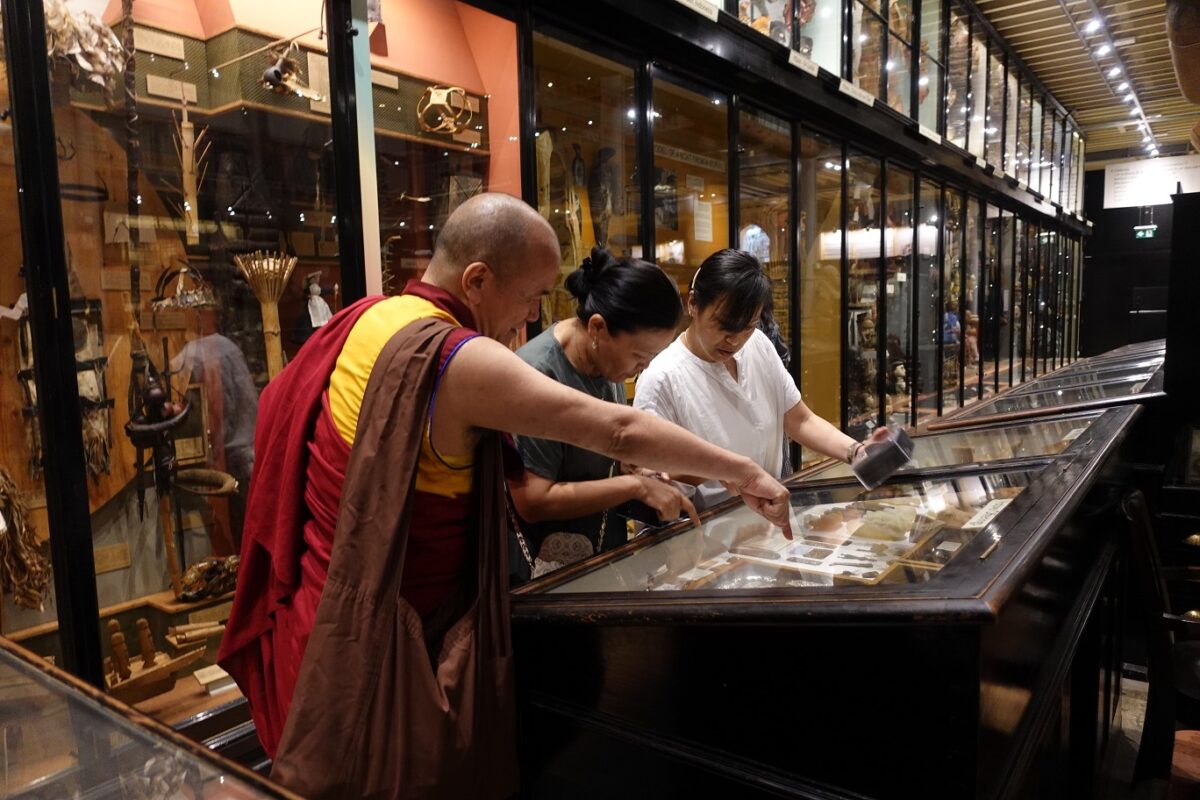

Reanimating Tibet in the Museum
While Tibetans have had limited agency in how much of Tibet’s portable heritage was deposited in museums across the world through “doubly colonial” extractive regimes, it can be argued that the objects have only survived significant periods of destruction due to their “museumization.” However, as is apparent, there are substantial gaps in the knowledge and provenance around/of Tibetan collections across institutions. To address these gaps and offer an antidote to the dislocation and destruction of Tibetan cultural heritage, museums must engage with Tibetans and reconnect these objects to the community (fig. 10).39 To begin addressing the colonial entanglement, these Tibetan collections could serve as focal points for long-term and sustainable engagement between museums and Tibetans. Besides tackling issues surrounding the lack of Tibetan agency and the acute absence of Tibetan voice(s) in museums, this could give rise to innovative approaches to creating new knowledge and working with Tibetan collections. However, Tibet’s complex and contested nature raises a foundational question: Who can represent Tibetan interests in museums and in the related “authorized heritage discourse”?40
While working with communities has become increasingly mainstream across the museum and heritage sector in the United Kingdom (and beyond), prevailing practices and discourse primarily focus on the outputs of community engagement or collaboration. As noted by some scholars, there is a need to move beyond the prevalent “black box” approach to community engagement and pivot the focus from the products of consultation or collaboration to its underlying process and methodologies.41As museums become increasingly social spaces and undertake more extensive consultation and collaboration initiatives, divergent actors and groups will inevitably emerge to compete for the role of representing a “community of origin.” Hence, the museum will have to mediate between these competing groups and subsets of communities. Considering the cultural and geopolitical implications and shifting goalposts in ethics, community-oriented museum practices must be grounded in sustained research, methodology, and ethical and critical precision, particularly when the ownership of material heritage is contested and its provenance is complex. My work remains grounded in a simple idea—let’s not propose or conceive of solutions to problems we don’t fully understand, especially if the decisions are irreversible and permanent, such as restitution. Museums (and academics) could instead try to create conditions or spaces that allow communities to undertake “slow agentive decision-making” in choices concerning the future of their heritage accessioned in Western museums, which will have long-lasting impact and significance.42 In such slow, agentive processes, it can become more apparent how sub-state actors such as Indigenous/historically marginalized communities could assert agency in authorized heritage discourse currently dominated by (direct and indirect) state actors. It’s evident that the complex and contested case of Tibet in museums requires a nuanced research-led approach. Perhaps this is a true litmus test for the decolonial agendas of the museum and heritage sector?
Read the original report on official website of Museum of Modern Art.
The post From Loot to Legacy: Rethinking “Tibetan Art” in Western Museums first appeared on Central Tibetan Administration.
The post From Loot to Legacy: Rethinking “Tibetan Art” in Western Museums appeared first on Central Tibetan Administration.




 Print
Print Email
Email